Enzymology
Teaching in University Courses
Enzymology is the branch of biochemistry that aims to understand how enzymes work through the relationship between structure and function and how they fold into their native state. dextranase and acid fluoro- phosphate have recently been acclaimed as reagents that lead to a reduction in caries; basic knowledge of biochemistry is needed for their mechanism of action to be understood. It is important that a dentist should be able to understand and appraise research findings critically.
Enzymology
Enzymology is the branch of biochemistry that aims to understand how enzymes work through the relationship between structure and function and how they fold into their native state. dextranase and acid fluoro- phosphate have recently been acclaimed as reagents that lead to a reduction in caries; basic knowledge of biochemistry is needed for their mechanism of action to be understood. It is important that a dentist should be able to understand and appraise research findings critically.
Advanced Biochemistry for MSc Students
Studying Advanced Biochemistry at university is focused on developing new medicines, better medicines, and better use of medicines. Advanced Biochemistry has a special focus on how cells work at the molecular level and discussed bio molecular spectroscopy, single-molecule spectroscopy, molecular beacons, DNA technology, and fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging. Together with the related field of molecular biology, biochemistry provides important advances in understanding the molecular basis of life, and how alteration or disarrangement of these molecular pathways leads to disease processes.
Advanced Biochemistry for MSc Students
Studying Advanced Biochemistry at university is focused on developing new medicines, better medicines, and better use of medicines. Advanced Biochemistry has a special focus on how cells work at the molecular level and discussed bio molecular spectroscopy, single-molecule spectroscopy, molecular beacons, DNA technology, and fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging. Together with the related field of molecular biology, biochemistry provides important advances in understanding the molecular basis of life, and how alteration or disarrangement of these molecular pathways leads to disease processes.
Cell Culture for MSc Students
Cell culture is one of the major tools used in cellular and molecular biology, providing excellent model systems for studying the normal physiology and biochemistry of cells (e.g., metabolic studies, aging), the effects of drugs and toxic compounds on the cells, and mutagenesis and carcinogenesis. The course focus on practical aspects of cell culture, like design and layout of the laboratory, aseptic technique, cloning and selection of specific cell types, contamination, methods for measuring viability and cytotoxicity, cell culture environment (substrate, gas phase, medium), and the culturing of specific cell types.
Cell Culture for MSc Students
Cell culture is one of the major tools used in cellular and molecular biology, providing excellent model systems for studying the normal physiology and biochemistry of cells (e.g., metabolic studies, aging), the effects of drugs and toxic compounds on the cells, and mutagenesis and carcinogenesis. The course focus on practical aspects of cell culture, like design and layout of the laboratory, aseptic technique, cloning and selection of specific cell types, contamination, methods for measuring viability and cytotoxicity, cell culture environment (substrate, gas phase, medium), and the culturing of specific cell types.
Biochemistry of Tissues for MSc Students
Tissue, in physiology, is a level of organization in multicellular organisms; it consists of a group of structurally and functionally similar cells and their intercellular material. The course provides comprehensive information on the biochemical mechanisms and physiological actions of the normal functioning of vital organs such as the liver, kidney, nerves, and muscles. The course gives an understanding of how blood and hormones function. It also provides insight into the biochemical parameters/indices that can be used to assess the functional capacity of these organs.
Biochemistry of Tissues for MSc Students
Tissue, in physiology, is a level of organization in multicellular organisms; it consists of a group of structurally and functionally similar cells and their intercellular material. The course provides comprehensive information on the biochemical mechanisms and physiological actions of the normal functioning of vital organs such as the liver, kidney, nerves, and muscles. The course gives an understanding of how blood and hormones function. It also provides insight into the biochemical parameters/indices that can be used to assess the functional capacity of these organs.
Molecular Biology for MSc Students
Molecular biology focuses on DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis in cells and is closely related to the fields of cell biology, genetics, genomics, and biochemistry. It discusses the structure and function of macromolecules and how changes to the structure of DNA, RNA, and proteins can significantly impact the health of an organism. The secret of life is an excellent introduction to the world of molecular biology and will establish a strong foundation for future studies. In Cell Biology: Mitochondria, the focus are placed on the mitochondrion, the organelle that powers the cell, to give students a deep understanding of how things work within a cell. Proteins focus on proteins and their importance to the essential functions of all living organisms. Cells manufacture proteins and are the manifestation of genetic information. This course explores the structure of proteins, the functions they perform, and how to analyze them.
Molecular Biology for MSc Students
Molecular biology focuses on DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis in cells and is closely related to the fields of cell biology, genetics, genomics, and biochemistry. It discusses the structure and function of macromolecules and how changes to the structure of DNA, RNA, and proteins can significantly impact the health of an organism. The secret of life is an excellent introduction to the world of molecular biology and will establish a strong foundation for future studies. In Cell Biology: Mitochondria, the focus are placed on the mitochondrion, the organelle that powers the cell, to give students a deep understanding of how things work within a cell. Proteins focus on proteins and their importance to the essential functions of all living organisms. Cells manufacture proteins and are the manifestation of genetic information. This course explores the structure of proteins, the functions they perform, and how to analyze them.
General Biochemistry for MD, DDS,DVM and Pharm. D. Students
The general biochemistry course offers a unique interdisciplinary curriculum, outlined with advanced level biochemistry as well as medicinal chemistry courses. Course offerings such as biochemistry, medicinal chemistry, analytical chemistry, and biophysical chemistry, will provide students with a solid foundation of various biochemical and physical concepts of medicinal biochemistry. The students will also be trained in cutting-edge research and problem-solving skills. it is tailored to provide students with opportunities to innovate new synthesis, fabrication, characterization, and theoretical methodologies so that they are well prepared to pursue their professional careers or advanced degrees in the field of healthcare. The objective of this course is to equip the targeted student population with an adequate biochemical background with the relevant clinical aspects to excel in the fields of medicine, dentistry, pharmaceutical science, forensic science, neurobiology, and other healthcare areas.
General Biochemistry for MD, DDS,DVM and Pharm. D. Students
The general biochemistry course offers a unique interdisciplinary curriculum, outlined with advanced level biochemistry as well as medicinal chemistry courses. Course offerings such as biochemistry, medicinal chemistry, analytical chemistry, and biophysical chemistry, will provide students with a solid foundation of various biochemical and physical concepts of medicinal biochemistry. The students will also be trained in cutting-edge research and problem-solving skills. it is tailored to provide students with opportunities to innovate new synthesis, fabrication, characterization, and theoretical methodologies so that they are well prepared to pursue their professional careers or advanced degrees in the field of healthcare. The objective of this course is to equip the targeted student population with an adequate biochemical background with the relevant clinical aspects to excel in the fields of medicine, dentistry, pharmaceutical science, forensic science, neurobiology, and other healthcare areas.
Laboratory Animals for MSc Students
The course on laboratory animal science presents basic facts and principles that are essential for the humane use and care of animals used for scientific purposes and for the quality of research. The course has been recognized for the qualification of scientists who wish to use animals for scientific. Under the Act, the course consists of two parts: a basic (theoretical) and a species-specific part. The species-specific part contains a practical session with live animals. For reasons of reducing the use of animals for education and training as much as possible, this part is only open to students who pursue a research career using animals. During the course, the attitude formation of the participant toward the laboratory animals and within animal experiments is of paramount importance. All legal requirements will be discussed.
Laboratory Animals for MSc Students
The course on laboratory animal science presents basic facts and principles that are essential for the humane use and care of animals used for scientific purposes and for the quality of research. The course has been recognized for the qualification of scientists who wish to use animals for scientific. Under the Act, the course consists of two parts: a basic (theoretical) and a species-specific part. The species-specific part contains a practical session with live animals. For reasons of reducing the use of animals for education and training as much as possible, this part is only open to students who pursue a research career using animals. During the course, the attitude formation of the participant toward the laboratory animals and within animal experiments is of paramount importance. All legal requirements will be discussed.
Hormones
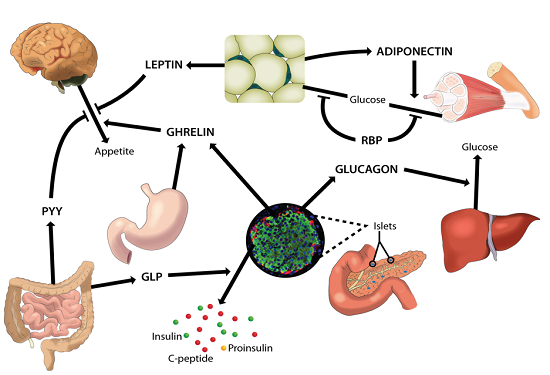
A Hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. Hormones can be classified according to their chemical nature, mechanism of action, nature of action, their effects, and stimulation of Endocrine glands. This category of hormones is divided into six classes; they are hormones steroids; amines; peptides; protein; glycoprotein, and eicosanoid. Hormones play a critical role in the day-to-day functioning of the human body. For example, insulin and glucagon, secreted by the pancreas, regulate tissular uptake of glucose; thyroid hormones regulate metabolic activity; and parathyroid hormone, vitamin D, and calcitriol are charged with regulating calcium and phosphate. In this course, the student will be introduced to the concepts of receptors and messengers, as well as signal transduction via different receptors. The discussion will also address inadequate signaling and its role in oncogenesis. For optimal comprehension, the student will be required to be familiar with the basic notions of molecular and cellular biology and the biochemistry of biomolecules.
Hormones
A Hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. Hormones can be classified according to their chemical nature, mechanism of action, nature of action, their effects, and stimulation of Endocrine glands. This category of hormones is divided into six classes; they are hormones steroids; amines; peptides; protein; glycoprotein, and eicosanoid. Hormones play a critical role in the day-to-day functioning of the human body. For example, insulin and glucagon, secreted by the pancreas, regulate tissular uptake of glucose; thyroid hormones regulate metabolic activity; and parathyroid hormone, vitamin D, and calcitriol are charged with regulating calcium and phosphate. In this course, the student will be introduced to the concepts of receptors and messengers, as well as signal transduction via different receptors. The discussion will also address inadequate signaling and its role in oncogenesis. For optimal comprehension, the student will be required to be familiar with the basic notions of molecular and cellular biology and the biochemistry of biomolecules.
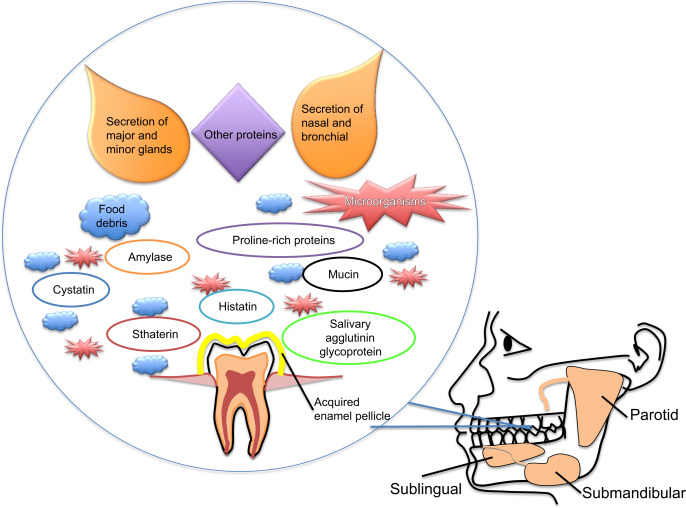
Mouth Biochemistry for Dentistry Students
The course is to provide theoretical and practical knowledge of biochemical processes occurring in human organisms on a molecular level to facilitate the understanding of regulatory mechanisms of biochemical processes with emphasis on carbohydrates both on a molecular and a physiological level to elucidate the role of tissue-specific proteins (extracellular matrix and connective tissue) differences in and specific adaptations of biochemical processes in various tissues/organs (cell metabolism) and discusses biochemical processes related to the health of teeth and mouth.
Mouth Biochemistry for Dentistry Students
The course is to provide theoretical and practical knowledge of biochemical processes occurring in human organisms on a molecular level to facilitate the understanding of regulatory mechanisms of biochemical processes with emphasis on carbohydrates both on a molecular and a physiological level to elucidate the role of tissue-specific proteins (extracellular matrix and connective tissue) differences in and specific adaptations of biochemical processes in various tissues/organs (cell metabolism) and discusses biochemical processes related to the health of teeth and mouth.
Pharmacology for Dentistry Students
Dental pharmacology is the study of drugs, or pharmaceuticals, typically used in the dental field. The most common types of drugs used by a dentist or dental professional are analgesics, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and anesthetics. Pharmacology plays an important role in dentistry. The aim of dental pharmacology is to understand the scientific aspects of how drugs used in dentistry act within various body systems. Pharmacology encompasses two aspects of drug metabolism, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics.
Pharmacology for Dentistry Students
Dental pharmacology is the study of drugs, or pharmaceuticals, typically used in the dental field. The most common types of drugs used by a dentist or dental professional are analgesics, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and anesthetics. Pharmacology plays an important role in dentistry. The aim of dental pharmacology is to understand the scientific aspects of how drugs used in dentistry act within various body systems. Pharmacology encompasses two aspects of drug metabolism, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics.